In an era of rapid urbanization, rising housing costs, and the pressing need for climate resilience, sustainable communities are emerging as a beacon of hope. These thoughtfully designed spaces prioritize ecological balance, self-sufficiency, and social inclusion, providing a model for how humanity can harmonize with the planet while addressing housing challenges. At the core of this vision lies the revolutionary concept of off-grid living systems, which redefine what it means to live sustainably and design affordably. One of the most innovative aspects of these communities is their emphasis on integrated food production, particularly through Earthship Walipinis, which enable year-round massive food production.

Sustainability as a Foundation
Sustainability is no longer just a trend — it’s a necessity. Communities of the future must integrate systems that reduce environmental impact, conserve resources, and foster a connection with nature. This begins with the buildings themselves. Each building in a sustainable community is designed to operate entirely off-grid, eliminating reliance on traditional utilities and significantly lowering costs for residents.
Off-grid systems are more than just a technical innovation; they are a paradigm shift in how we live. By harnessing natural resources like sunlight, wind, and rain, these systems create a closed-loop environment where energy, water, and waste-water are managed independently and responsibly. The benefits extend beyond environmental gains to include economic savings, community resilience, and the empowerment of residents to take charge of their resource use.
Understanding Off-Grid Living Systems
The concept of off-grid living may seem futuristic, but its components are remarkably practical and achievable. Here’s a deeper look at the core systems that make this lifestyle possible:
1. Renewable Energy Solutions
Off-grid energy systems are anchored in renewable resources. Solar power, often referred to as “the king of renewables,” plays a central role in powering these communities. In areas with abundant sunshine, like many parts of the Southwest, solar panels provide an almost limitless supply of clean energy. When complemented by wind turbines and, where feasible, micro-hydro systems, communities can create a diverse and resilient energy portfolio.
Battery storage technology has also advanced significantly, enabling residents to store excess energy for use during cloudy days or at night. This not only reduces dependency on fossil fuels but also ensures consistent power supply, even in isolated locations.
2. Water Independence
Water scarcity is a global concern, but sustainable communities are designed to be water-wise. Rainwater harvesting systems capture precipitation, storing it in tanks for household and community use. Greywater recycling systems treat and reuse water from sinks, showers, and laundry for irrigation, flushing toilets and other non-potable applications, reducing overall water demand.
One of the most innovative systems is the use of botanical cells — natural filtration systems that process greywater and blackwater (sewage) without leaching contaminants into the ground. These systems support lush gardens, producing flowers, herbs, and even food, while turning waste into a valuable resource. For added security, backup water supplies can be integrated, sourced from local aquifers or community partnerships. This allows for little to no wells depending on annual precipitation.
3. Sustainable Food Production with Earthship Walipinis
Food security is a cornerstone of self-sufficient communities, and Earthship Walipinis are a game-changing innovation in sustainable agriculture. These in-ground greenhouses are designed to leverage thermal mass and passive solar energy, maintaining a stable, warm climate ideal for year-round food production, even in harsh weather conditions.
Earthship Walipinis allow communities to grow a variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs without relying on external supply chains, reducing food miles and ensuring freshness. These systems can also integrate aquaponics for fish farming, creating a closed-loop ecosystem that maximizes productivity. Permaculture principles guide all farming practices, ensuring the land is regenerated and biodiversity is preserved. By incorporating these innovative greenhouses, sustainable communities can not only feed their residents but also supply local restaurants, markets, and even nearby communities with fresh, organic produce.
Animal synergy practices further enhance food production, with livestock playing an essential role in natural fertilization and pest control. Together, these systems create a robust, resilient food supply that underscores the self-reliant ethos of off-grid living.
4. Waste Management Reimagined
Traditional waste disposal methods are not only inefficient but also harmful to the environment. Off-grid communities flip this script by adopting holistic waste management practices. Organic waste is composted, returning valuable nutrients to the soil. Greywater and Blackwater botanical cells process sewage in a safe, closed-loop system that eliminates pollutants and generates life-giving resources. Recycling programs and community education further reduce landfill contributions.
Prioritizing Affordability
While the technology and systems behind off-grid living may seem high-tech, their implementation can be remarkably cost-effective. Affordable housing must lead the way in any sustainable community, ensuring that these benefits are accessible to everyone. By eliminating utility bills through self-sufficient systems, affordable housing can start as low as $500 per month, offering a transformative solution for individuals and families facing financial pressures.
Affordable senior housing further extends these benefits to older generations, providing safe, comfortable homes for retirees. Workforce housing supports essential workers, such as teachers, healthcare providers, and first responders, ensuring they can live close to their jobs. Market value homes, while designed for higher-income residents, also contribute to the overall financial sustainability of the community.
A Blueprint for the Future
What sets these communities apart is their focus on holistic design. Sustainability is not just about the environment; it’s about creating spaces where people can thrive. Community gardens, amphitheaters, and shared cultural spaces encourage collaboration and interaction. Schools and wellness centers provide education and healthcare rooted in sustainable practices. Senior housing ensures multigenerational living which connects the wisdom and knowledge of our elders, fostering connection and support.
With Earthship Walipinis at the center of food production, residents are connected to their environment in a deeply meaningful way, experiencing firsthand the benefits of growing and consuming fresh, sustainable food. These greenhouses also strengthen the community’s resilience by reducing dependency on external food systems, creating a local economy that benefits everyone.
Why Sustainable Communities Matter Now
The challenges of climate change and housing inequality require bold, innovative solutions. Sustainable communities, with their emphasis on off-grid systems, integrated food production, and affordable living, offer a scalable, replicable model for addressing these challenges. They show us that it is possible to create spaces that are not only environmentally responsible but also economically accessible and socially inclusive.
As we look to the future, the question is no longer whether we can afford to make these changes—it’s whether we can afford not to. By prioritizing affordability, integrating Earthship Walipinis, and fostering vibrant communities, we have the opportunity to redefine how we live, work, and connect with one another. Together, we can build a world where sustainability is not just a goal but a way of life.
Together We Are Strong.

Pangea Biotecture is an architectural design and construction firm
providing sustainable buildings for residential, commercial and government use.
We are specialists in Modern Off-Grid Designs, Systems and Construction.
As we stand on the brink of a pivotal era, it is evident that our approach to design and construction must evolve. Pangea Biotecture was born out of a profound commitment to fostering sustainability in every aspect of our lives. The name “Pangea” itself, derived from the supercontinent that once united Earth’s landmasses, reflects our vision of a united effort to create a sustainable future. Together We Are Strong.
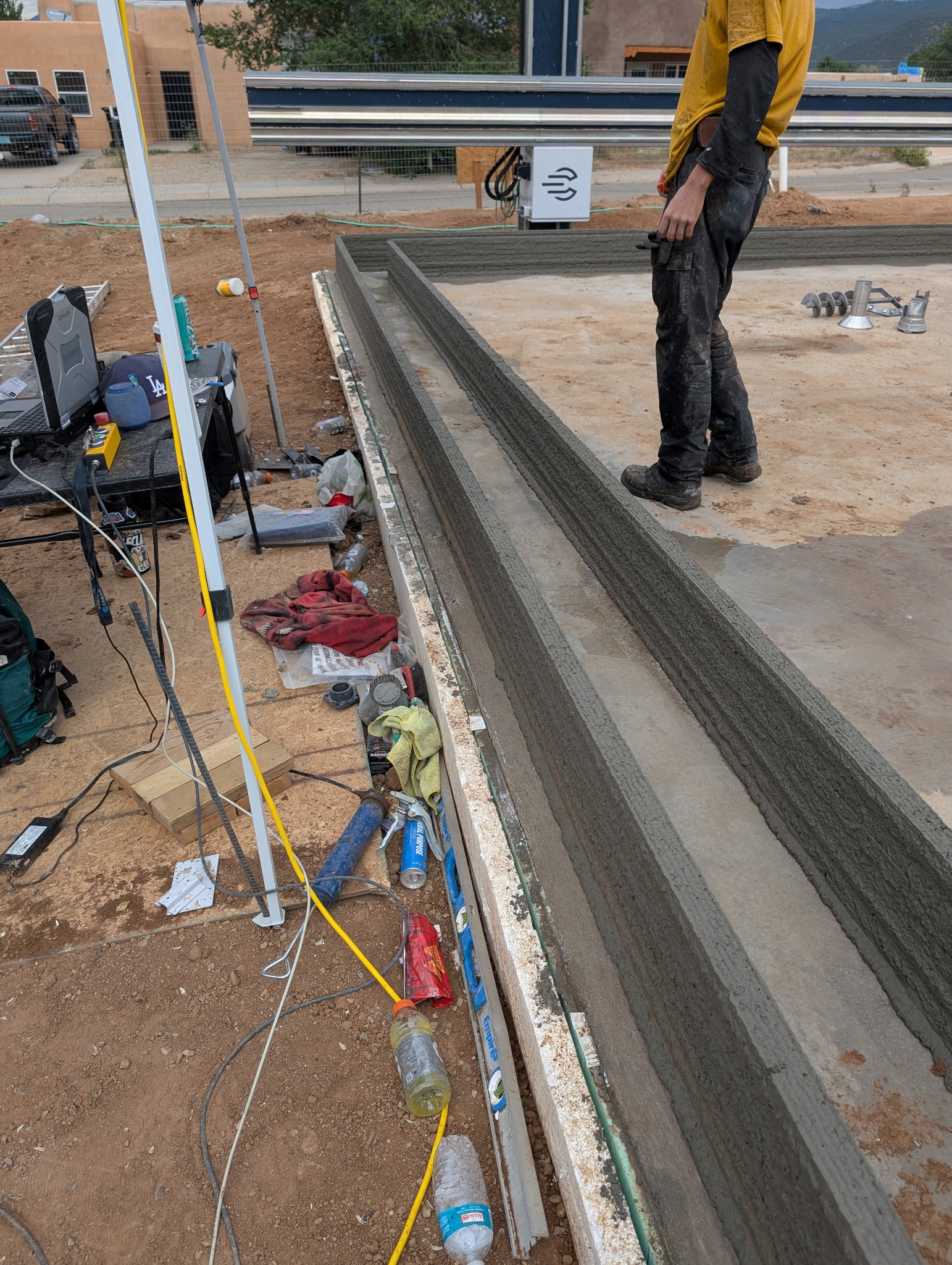





Have you ever done rammed earth construction?